Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly being embedded in products, services, and systems across many sectors. As its use expands, so do the risks — not just technical failures, but ethical, legal, social, and reputational hazards. Recognizing this, the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) developed the AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) as a voluntary guidance to help organizations conceive, design, deploy, and monitor trustworthy and responsible AI systems.
The AI RMF is designed to support alignment and interoperability with other risk management or governance frameworks, rather than replacing them. In 2024, NIST also published a Generative AI Profile to help organisations deal with unique risks posed by generative AI systems.
What is the AI RMF?
At its core, the AI RMF:
- Is voluntary and non-sector-specific, meaning organizations of any size or domain can adopt it.
- Aims to embed trustworthiness into AI systems — ensuring they are valid, reliable, secure, fair, transparent, accountable, resilient, and privacy-enhancing.
- Encourages organizations to treat AI risk management as an ongoing lifecycle activity rather than a one-off compliance exercise.
- Provides a core structure (functions, categories, subcategories) that organizations can adapt or align with their existing governance frameworks.
- Includes supporting materials such as the AI RMF Playbook, Roadmap, Crosswalks, and Use-Case Profiles to guide adoption.
In simple terms: Part 1 of the framework helps define what “trusted AI” means and what risks need attention, while Part 2 gives actionable steps to manage them.
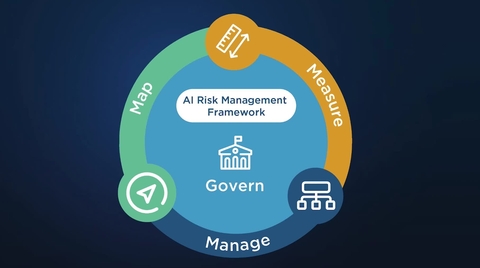
Core Structure: Four Key Functions
The heart of the AI RMF is its Core, which is built around four interrelated functions. These are not strictly sequential phases, but activities that should be iterated and revisited throughout the AI lifecycle.
| Function | Purpose / Focus | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Govern | Establish accountability, policies, and culture around AI risk | Define governance structures, roles, responsibilities, policies, and oversight |
| Map | Understand the context, scope, and potential risks of a given AI system | Identify boundaries, stakeholders, foreseeable harms, and scenarios |
| Measure | Assess and monitor risks systematically | Use qualitative and quantitative methods, define metrics, validate and test |
| Manage | Take actions to mitigate, transfer, accept, or monitor risks | Prioritize risk responses, apply controls, monitor outcomes, and update processes |
Governance is foundational — without governance, sustainable risk practices are difficult.
Map ensures context is clear: risks vary by domain, regulation, and stakeholders.
Measure acknowledges that some risks require qualitative judgement rather than numbers.
Manage focuses on prioritization and iteration as AI systems and risks evolve.
Trustworthiness and Risk: Key Concepts
Before applying the four functions, organizations are encouraged to reflect on two key areas: trustworthiness attributes and risk categories.
Trustworthiness attributes include:
- Validity and reliability
- Safety, security, and resilience
- Transparency and explainability
- Privacy protection
- Fairness and bias mitigation
- Accountability and governance
Common AI risk categories include:
- Bias and unfair outcomes
- Model drift and degradation
- Adversarial attacks or manipulation
- Privacy violations
- Misuse or unintended use
- Legal, compliance, or intellectual property risks
- Systemic or societal impacts
The framework emphasizes identifying and prioritizing the most relevant risks in context.
Profiles, Playbooks & Supporting Materials
To move from theory to practice, the AI RMF is supported by additional resources:
- Use-Case Profiles: Tailored guidance for specific applications (e.g. hiring, healthcare, generative AI).
- Playbook: Step-by-step guidance, worksheets, and examples.
- Roadmap: Long-term planning advice to evolve AI risk practices.
- Crosswalks: Mappings to other frameworks like cybersecurity or privacy standards.
- Perspectives: Domain-specific or stakeholder-focused best practices.
These tools make the framework more practical and adaptable.
Benefits & Challenges
Benefits
- Promotes systematic and proactive risk management.
- Provides a shared language for AI governance across teams.
- Supports building and maintaining trustworthy AI systems.
- Scales to organizations of any size or maturity.
- Helps demonstrate accountability to regulators, customers, and partners.
Challenges
- Requires customization — it’s not a “plug and play” checklist.
- Measuring social or systemic risks is complex.
- Needs strong governance culture and leadership buy-in.
- Must evolve continuously as AI and risks change.
- Integration with existing governance processes can be difficult.
Conclusion
The AI Risk Management Framework is not a rigid standard, but a flexible guide to help organizations build trustworthy AI while managing uncertainty and risk responsibly. By focusing on governance, context, measurement, and management, it provides a structured yet adaptable approach to handling AI risks.
For organizations investing in AI, adopting the AI RMF is not just about compliance or risk reduction — it is a step toward building confidence, accountability, and long-term trust in AI systems.